Integrate non-product content
Search Studio lets you index content from various sources besides product catalogs: website content, FAQs, videos, and more.
Step 1: Select a project
Make sure you're in the correct project. The project name is displayed at the top of the screen in Search Studio.
If you don’t have a project set up yet, go to Data Platform, create a project folder, and then return to Search Studio.
Step 2: Choose your data source
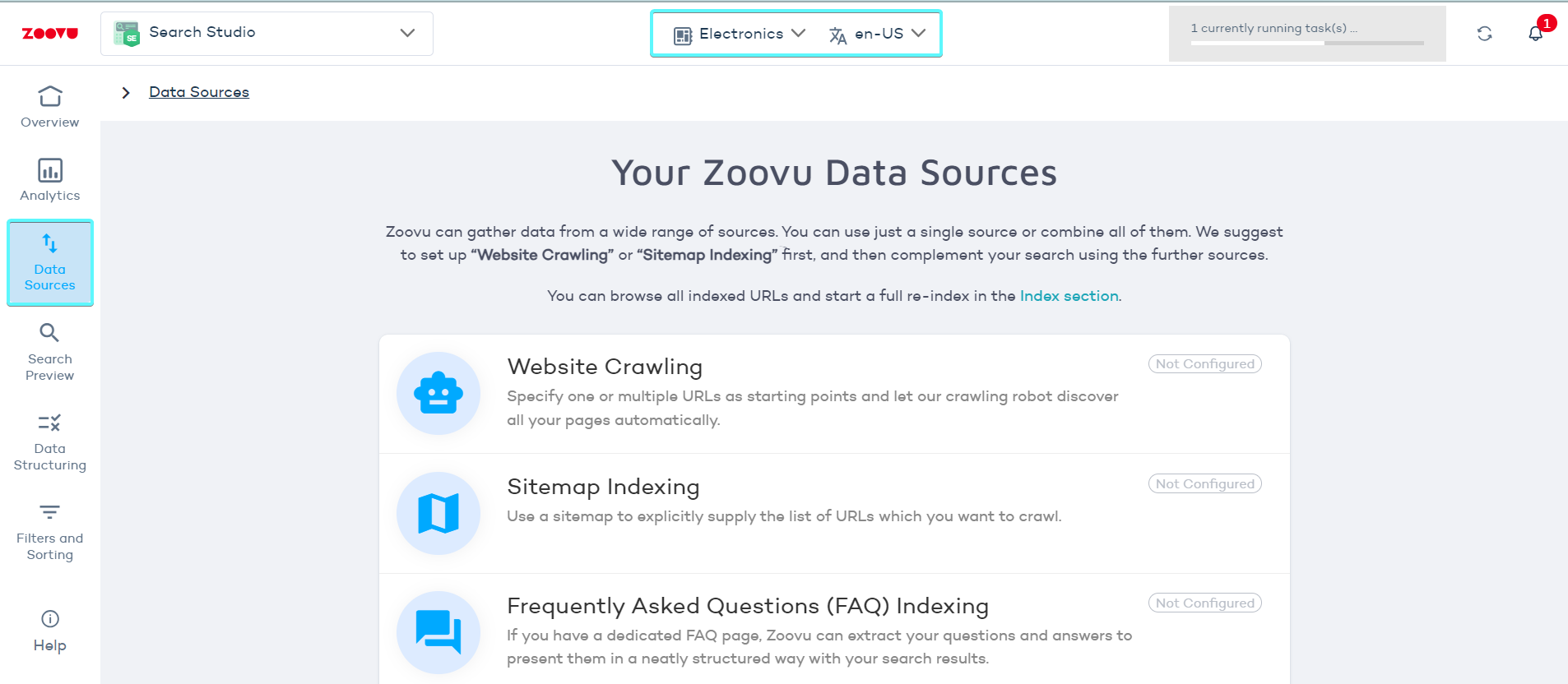
In Search Studio > Data Sources, you’ll find several indexing options. Select one or combine multiple options based on your needs. Here’s what each option does and how to use it effectively:
Sitemap indexing
If your website is large or has complex navigation, using a sitemap will help you avoid missed pages or irrelevant content.
A sitemap is a precise list of URLs you want to index. It helps the crawler find and index all the important pages on your site. Make sure your sitemap XML file is correctly formatted by following these guidelines.
- Go to Data Sources > Sitemap Indexing.
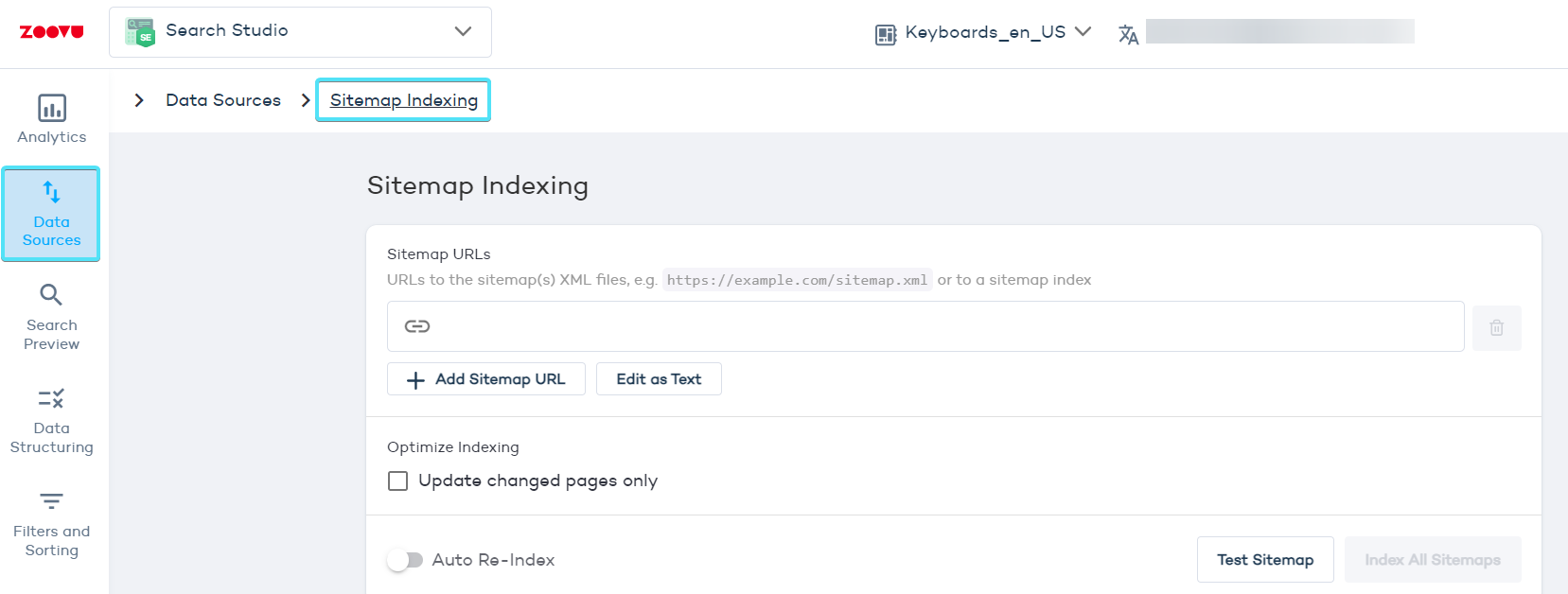
- If a valid sitemap is detected, the crawler will automatically pick up the URLs listed.
- If it's not detected, provide the URL to your sitemap and press Test Sitemap.
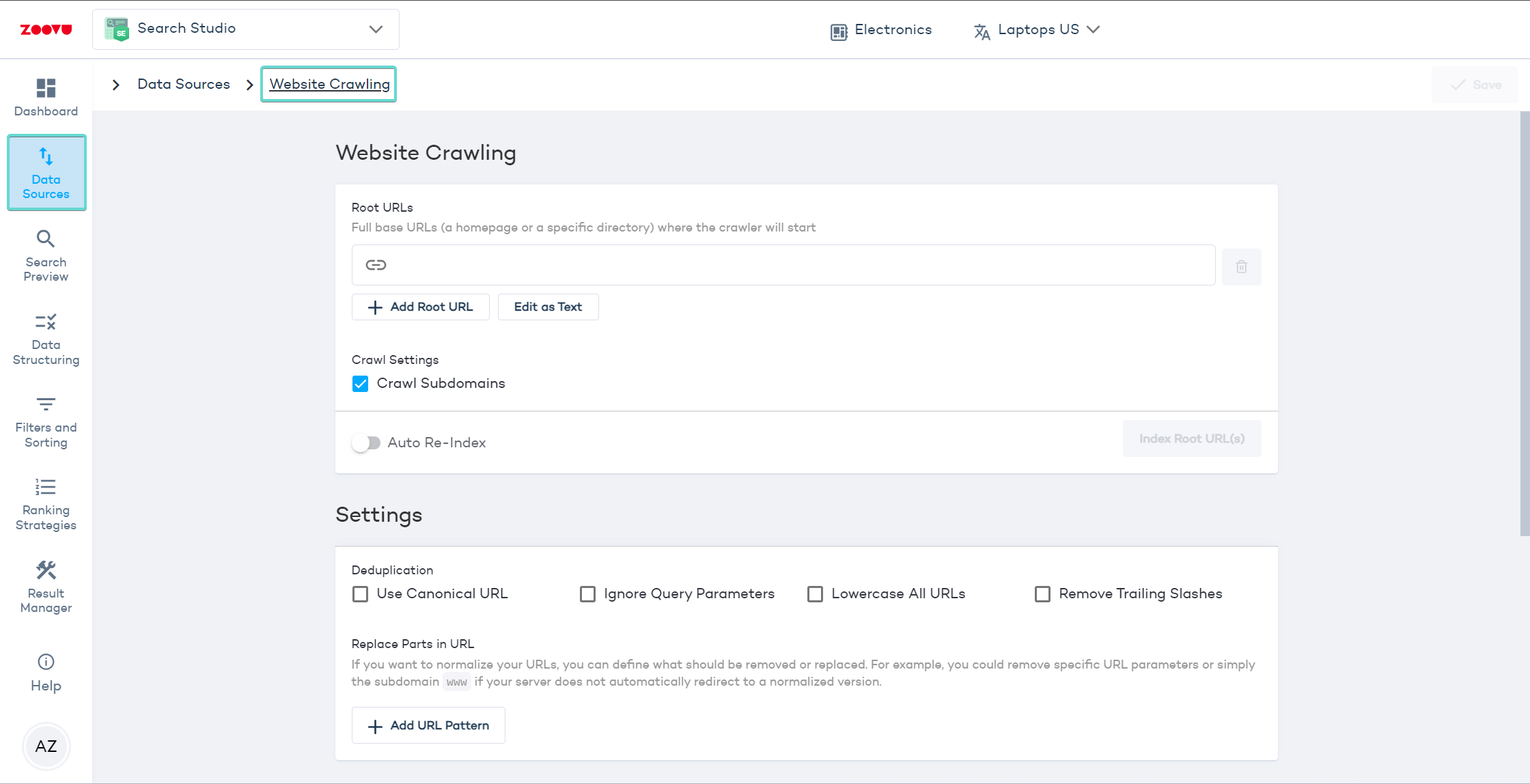
Activate the following settings to avoid the indexing of duplicate content:
- Use Canonical URL: The crawler uses the canonical URL from page links as the primary URL, preventing duplicate content issues.
- Ignore Query Parameters: This setting makes the crawler ignore URL query parameters that don’t change the page content, like session IDs or tracking codes.
- Lowercase All URLs: This standardizes all URLs to lowercase, avoiding indexing the same URL with different cases as separate pages.
- Remove Trailing Slashes: A trailing slash is the forward slash
/at the end of a URL. Enabling this option helps you maintain consistency in indexing.
Click "Test Sitemap" to see how many URLs Search Studio discovered. (If the number of URLs looks wrong, double-check your sitemap file for errors or omissions.)
Website crawling
The crawler will visit the root URL and follow all links to other pages, adding them to your index.
- Log in to Search Studio.
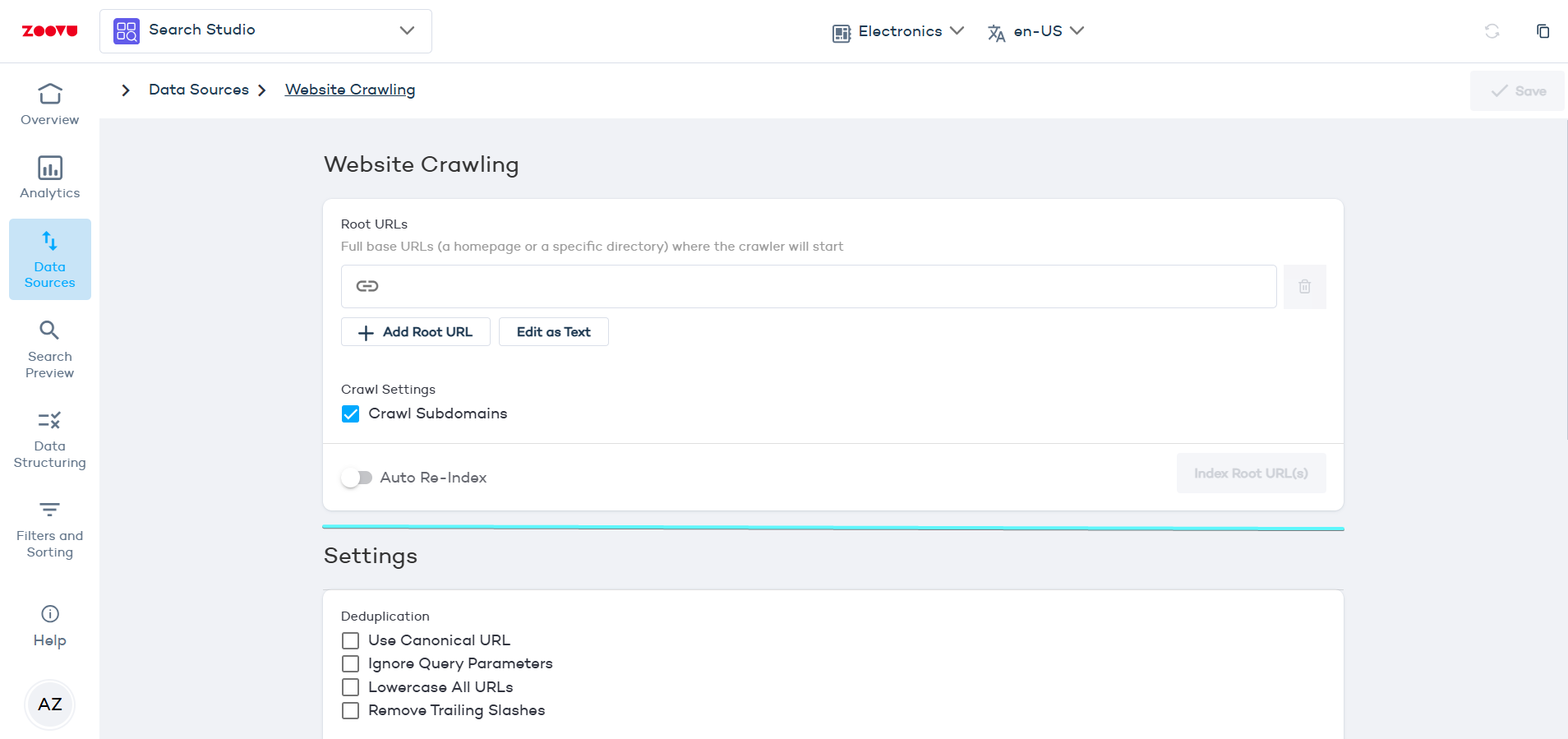
- Navigate to Data Sources > Website Crawling.
- Enter your root URL (e.g., your homepage) and click "Index".
- Click the "Save" button in the top right corner.
Start with the homepage or a high-level URL that links to most of your content. Avoid starting with deeply nested pages.
Wait until a full crawl is complete to check the number of indexed sites and documents.
Root URLs are the starting points for the crawler. Enter full base URLs - such as a homepage or a specific directory, from where the crawler will begin its operation. For example: https://zoovu.com.
URL List
You can manually supply a static list of URLs you want to index. Use this option if your content is limited and you know exactly which pages should be included. For example, use it for campaign landing pages or small microsites.
Save your settings
Once you’ve made adjustments, click Save in the top-right corner to apply your changes.
Indexing time depends on the amount of content. Larger websites take longer to process. The progress and results are displayed on the Data Sources page.
Data sources and indexing
Treat crawler and sitemap as two doors into one indexing system. Settings under Data sources > Crawling → crawl website are global. Any change there applies to all sources.
Edit once, affects both. Update an include/exclude pattern (e.g., blacklist /blog/) in crawler settings → sitemap-based indexing will honor it too. The reverse is also true.
Single-URL crawls still follow the rules. When you trigger Index log → Crawl URL, the global rules apply. A URL blocked by your blacklist won’t be indexed, even if you try to crawl it directly.
Plan rules to fit all sources. Create allow/deny patterns that work for both the crawler and the sitemap. Don’t rely on per-source exceptions.
Verify before a full run.
Add or adjust patterns in crawl website.
Test with a few representative URLs in Index log.
Check results; if a URL is skipped, look for a matching deny rule.
Re-run the source once the rules behave as expected.
Common examples
Need only product pages? Allow /p/ and deny everything else (/*), then add specific allows as needed.
Want to exclude out-of-stock pages? Add a deny pattern that matches their URL format; both crawler and sitemap will skip them.
Trying to force-index a denied URL? Remove or narrow the deny rule first, then re-crawl.
When you truly need different rules Global crawling rules can’t vary by source. If two very different strategies are required (e.g., strict rules for crawler, permissive for sitemap), consider splitting the workload across separate environments/projects, or sequence runs by temporarily changing the global rules and reverting after the targeted crawl.