Product relations
With the Product Relations functionality within the Zoovu Data Platform you can implement cross- and up-selling strategies to recommend alternatives or add-ons, increasing your average order value. You have the flexibly to automatically display alternative or complementary products either on your search result page, product detail pages or Zoovu experiences.
Create a product relation
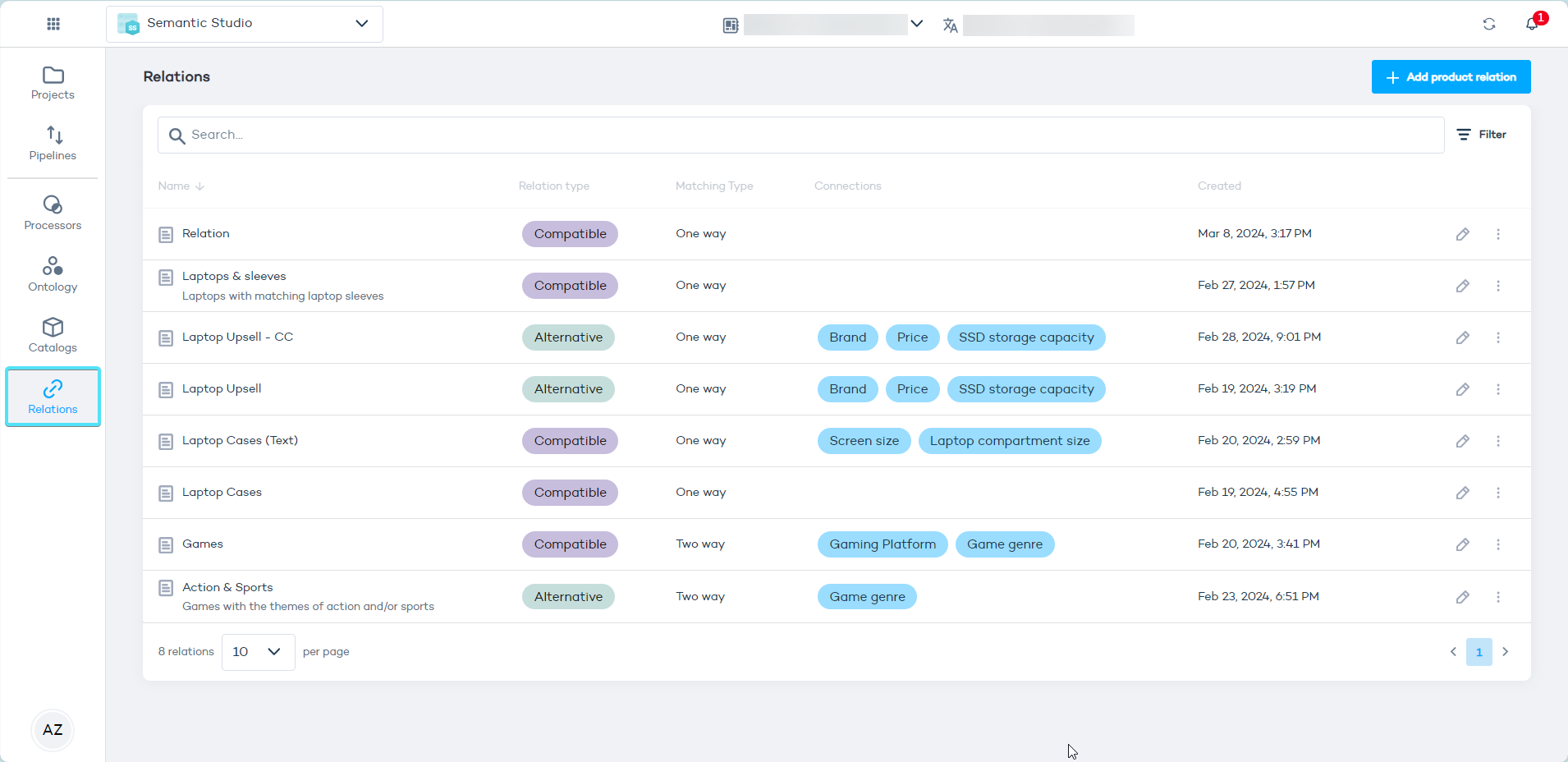
- In the Data Platform, access your account and navigate to "Relations" in the left-hand menu:
-
Click "Add product relation" to start configuring your relation.
-
Customize the following settings:
-
Name - Name for the product relations configuration.
-
Relation type - Select the relation type:
- Compatible: relationship between products that are compatible with each other, such as laptops and mice.
- Alternative: relationship between similar products, such as different models of laptops available at varying price points.
-
Description - A clear and recognizable label to easily identify the nature of the relationship.
-
Two-way matching: Select if the product relationships should be bi-directional.
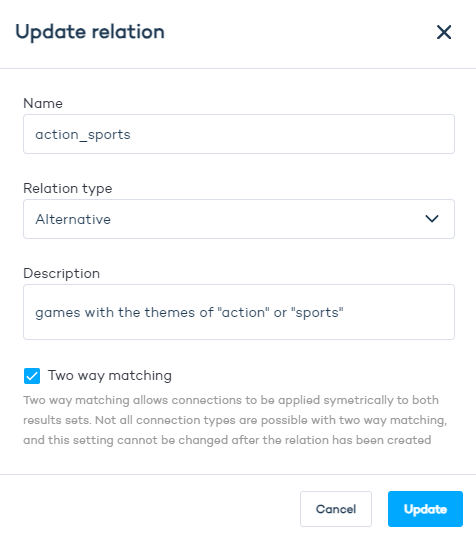
Avoid using "Two-Way Matching" for significantly different product sets, like laptops and laptop cases. It's logical for customers looking at laptops to see laptop cases as suggestions, but not the reverse.
Configure a product relation
The configuration panel consists of:
- Two lists of products from the catalog(s) linked to your Data Platform Project: later referred to as the left-side set and the right-side set. (The same products are listed on the left and on the right side until you filter the results).
- A "Filter" function allowing you to establish rules for which products should be displayed on the list.
- A "Sort" function, which lets you establish a descending or ascending order based on attributes such as price (e.g. from cheapest to the most expensive).
- A search bar allowing you to look up products by entering a text string, e.g. "laptops" or "games".
- A "Show matching" button next to each product, allowing you to view the connections established between this item and the others.
- A "Connection" button in the middle, which opens up a menu where you can configure relationships between products.
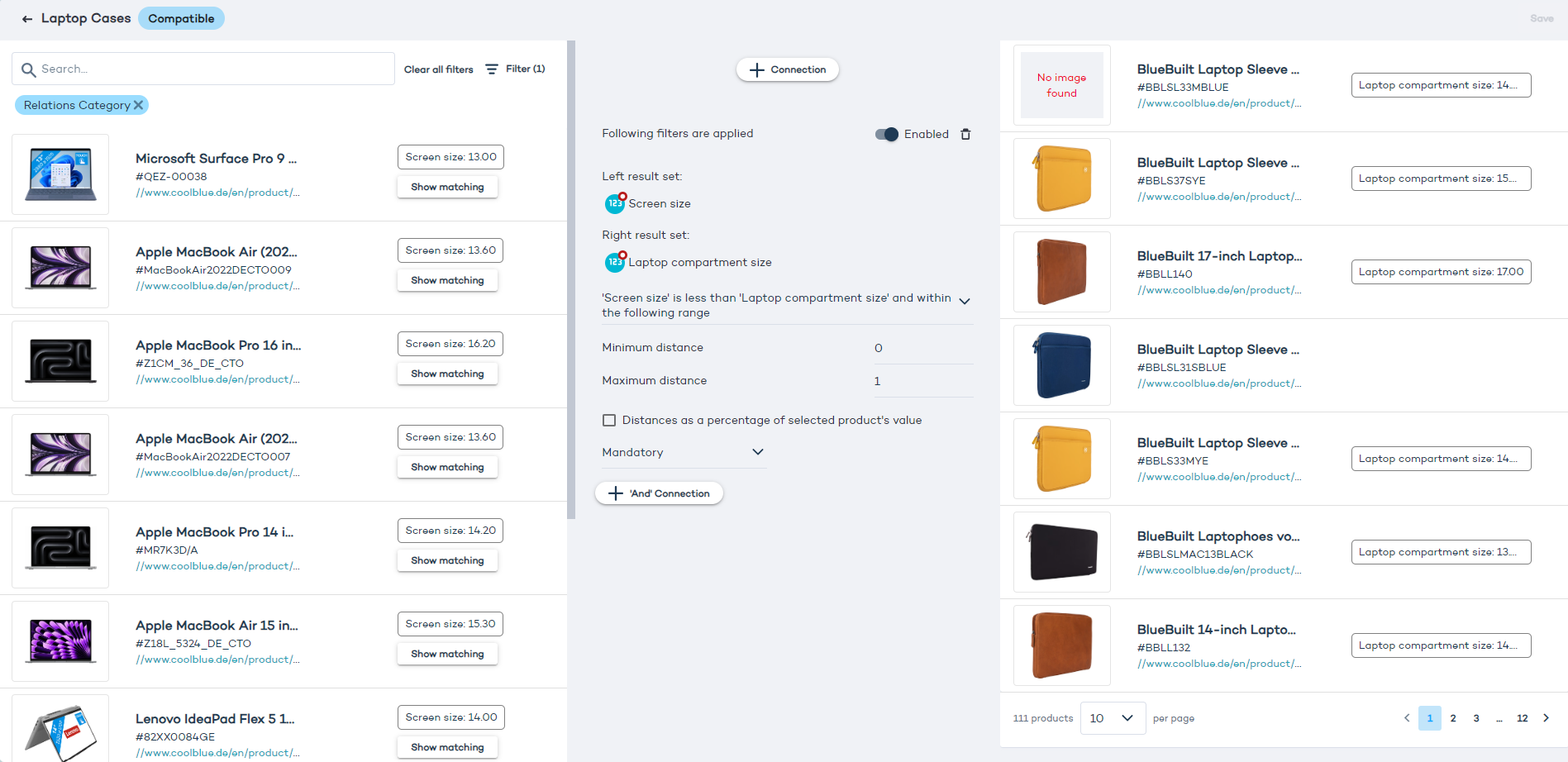
For each product to display in a way you can see in the image above, the catalog must contain all necessary information, such as product image, name, URL, and all relevant attributes (e.g. "width" for laptops or "genre" for games).
To see more information on each product, such as the Product Facts pulled from the catalog, click on its image.
Filter products
To find the right set of products from your catalog (e.g. a specific genre of games or laptops priced above 1000 USD), create a filter.
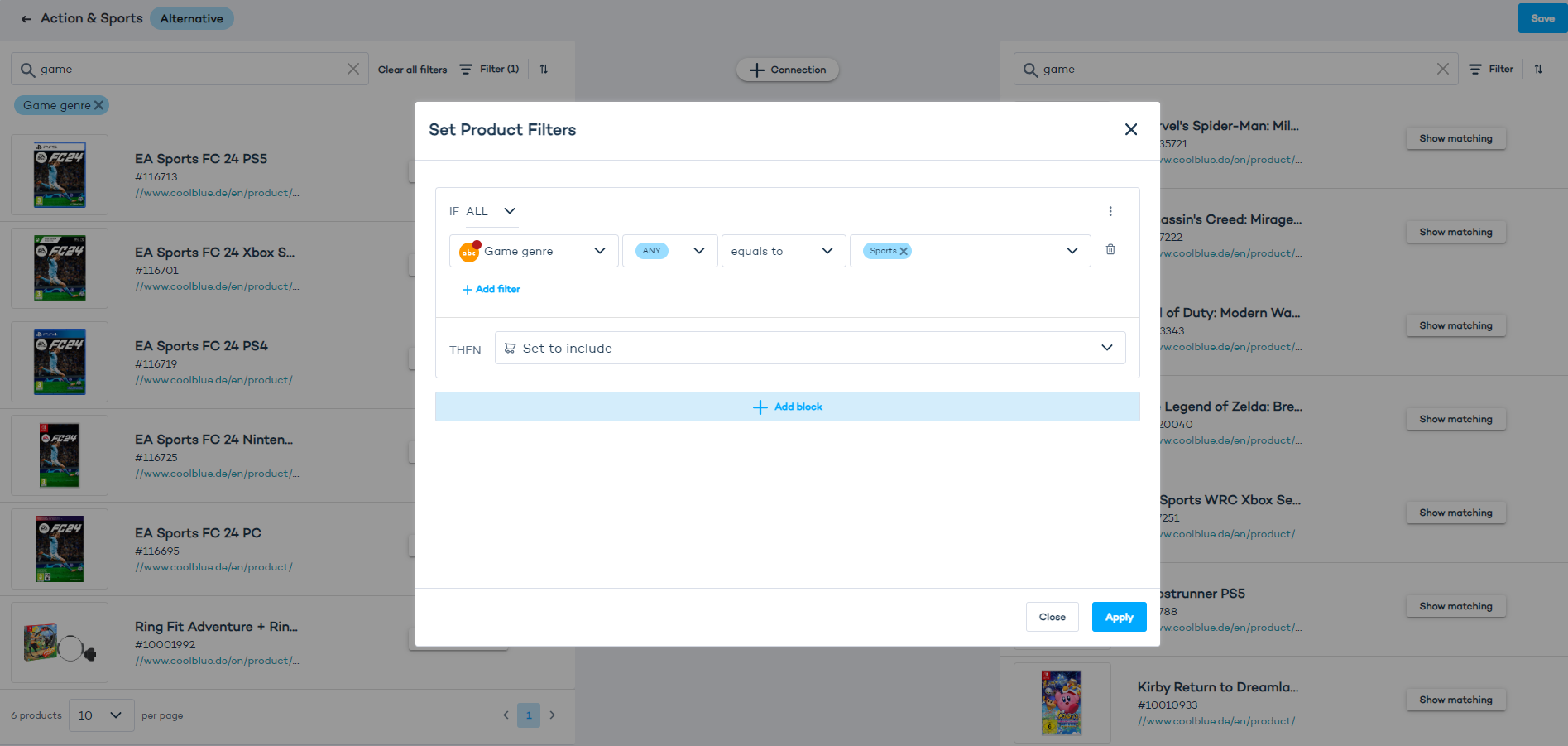
Each filter consists of blocks. Click "Add block" to define a rule consisting of:
- A product attribute (e.g. game genre).
- Comparison operator with four options: "equals to" or "not equal to" / "exists" or "does not exist".
- Value (this corresponds to attributes, e.g. "Sports" is one of the values available for the "game genre" attribute in our product catalog).
- "THEN" operator with two options: "Set to include" or "Set to exclude". (When it's set to exclude, it will hide the products with a given value.)
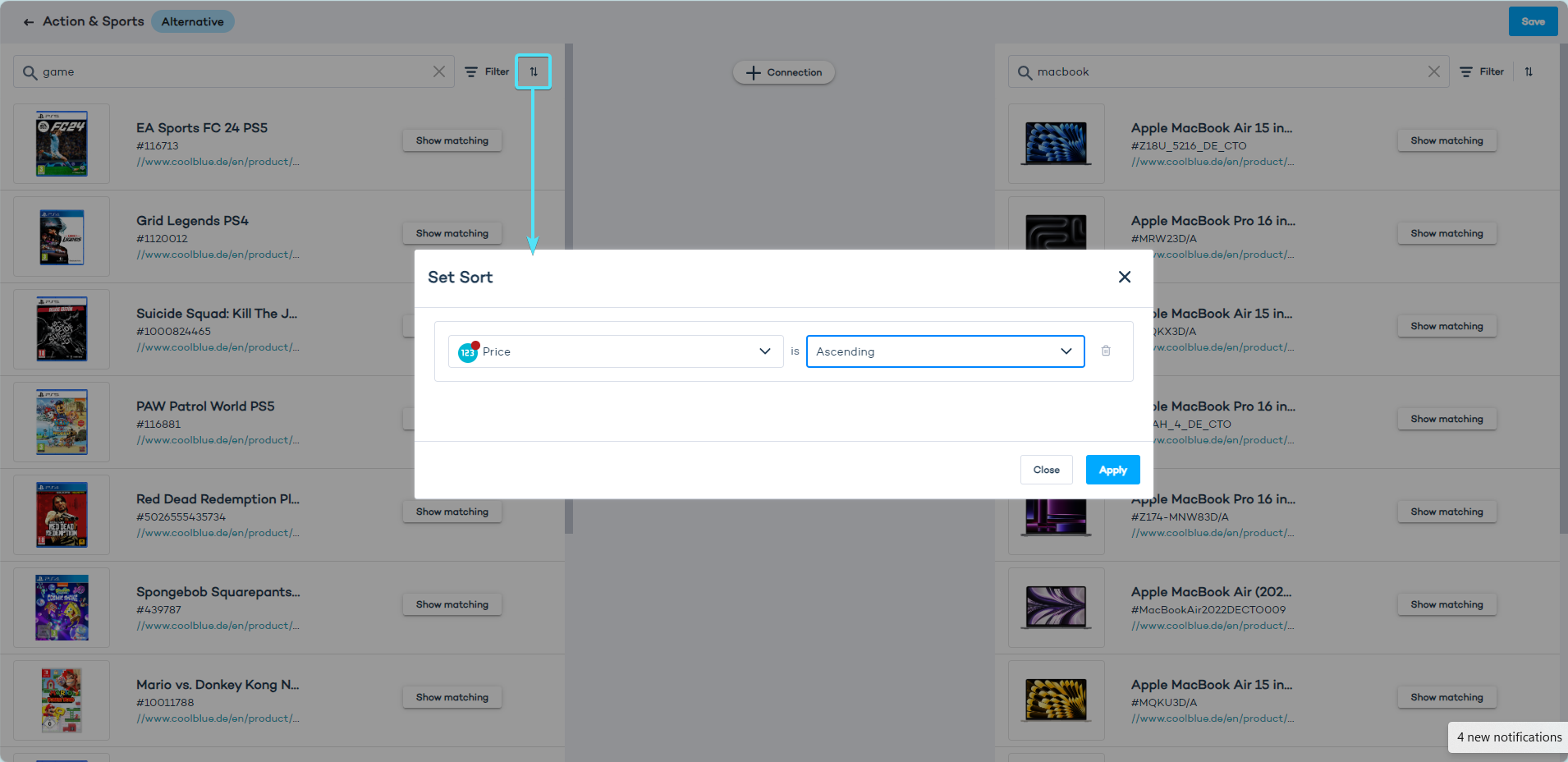
Sort products
Sorting is available for numeric product attributes, such as "Price". You can create an ascending or descending order. In the example below, we sort the products from those with the lowest price value to those with the highest.
Create a Product Relation for compatible products
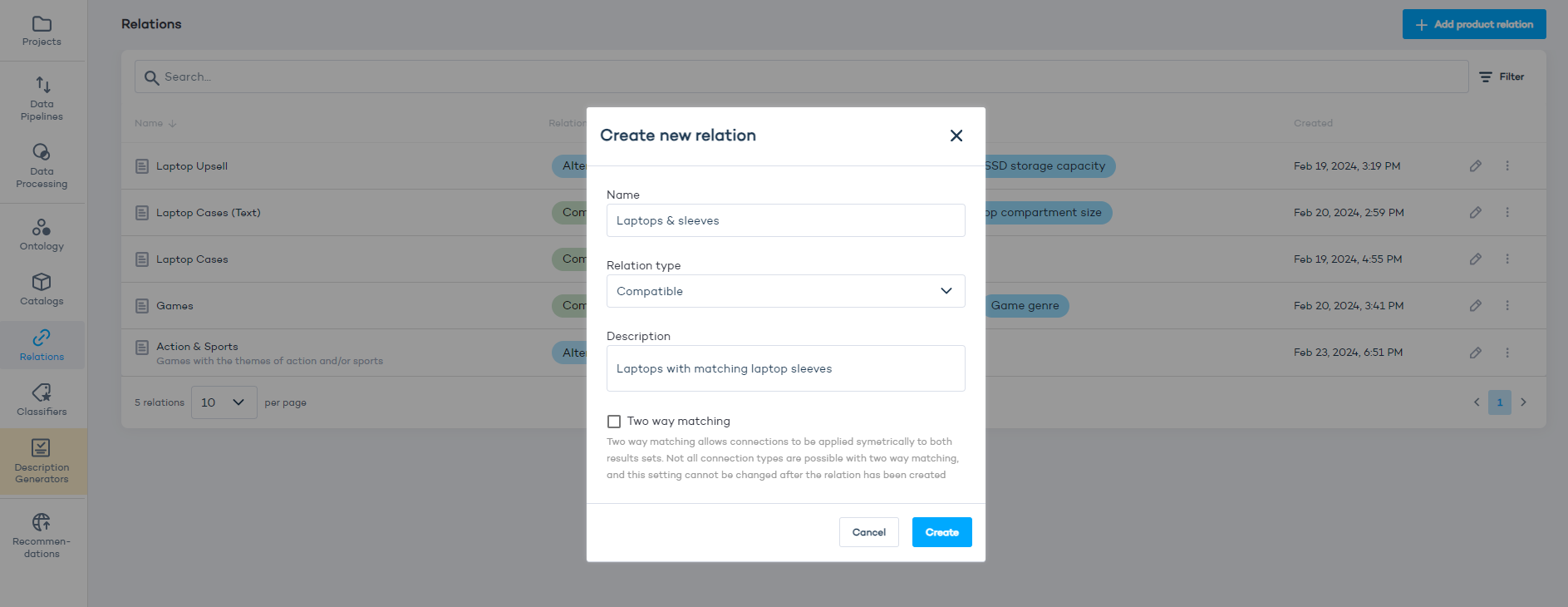
- Click "Add product relation" in the main Relations panel.
- Select a name, type: Compatible, and add a description.
- (Optional) Select "Two way matching" only if you want the recommendations to be applied to both sets of products.
- Click "Create".
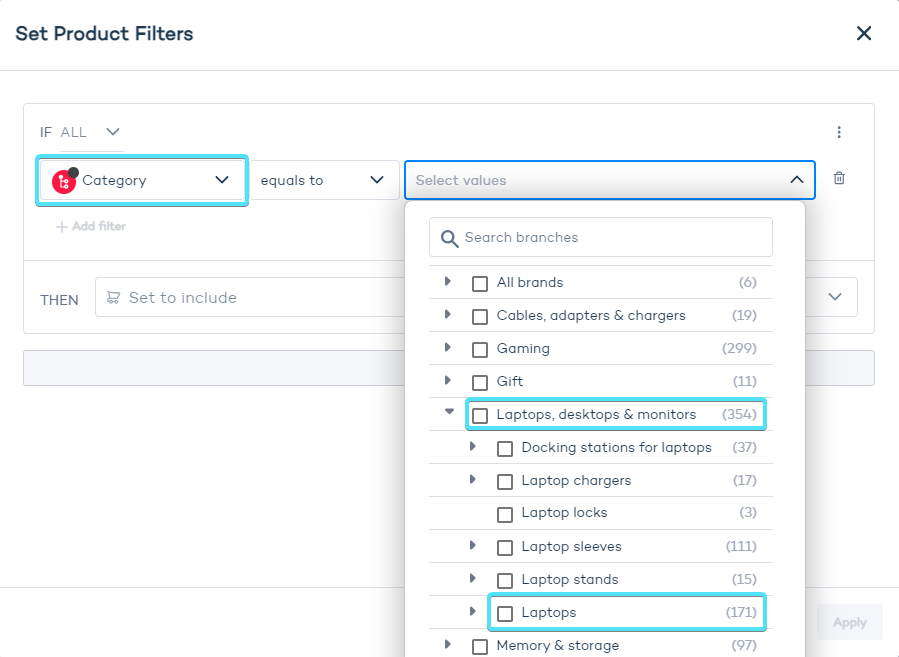
- Select left-side products which will be matched onto right-side products. Use the "Filter" option to narrow down the results.
- Add as many block to the filter as necessary for a precise result.
- The filter lets you select product attributes and values from your catalog. In the example below, we define the category of products by selecting "laptops" from multiple available values:
- Next, select products from the right column by adding a filter there. For example, select "Category" equal to "laptop sleeves".
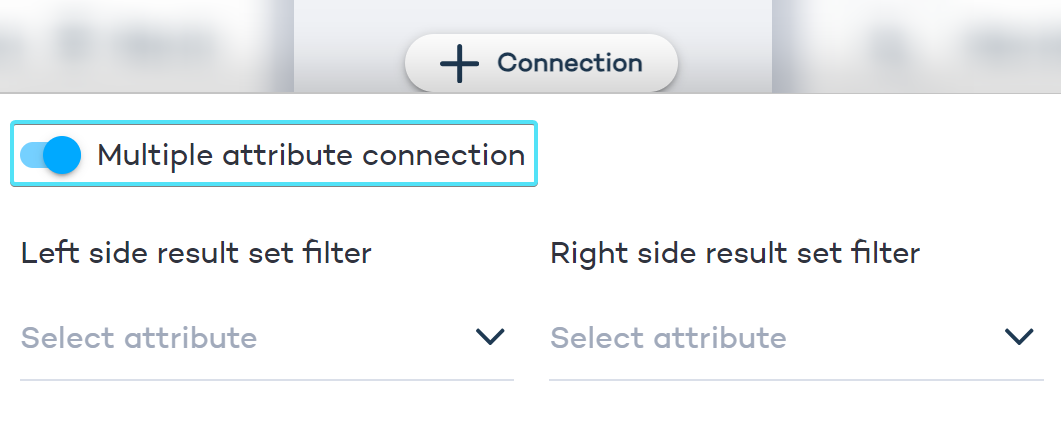
- Click the + Connection button in the middle of the screen.
- Enable Multiple attribute connection if you want to match selected attributes of left-side products onto different attributes in right-side products.
Disable "Multiple attribute connection" if you want to set the same attribute for both result sets, i.e. whenever you're matching the same type of products that share an attribute.
- Configure the left result set (the values for products featured in the left column, e.g. the laptops' screen size).
- Configure the right result set (the values for products featured in the right column, e.g. the laptop sleeves' size).
- Click "Save" in the top right corner of the screen.
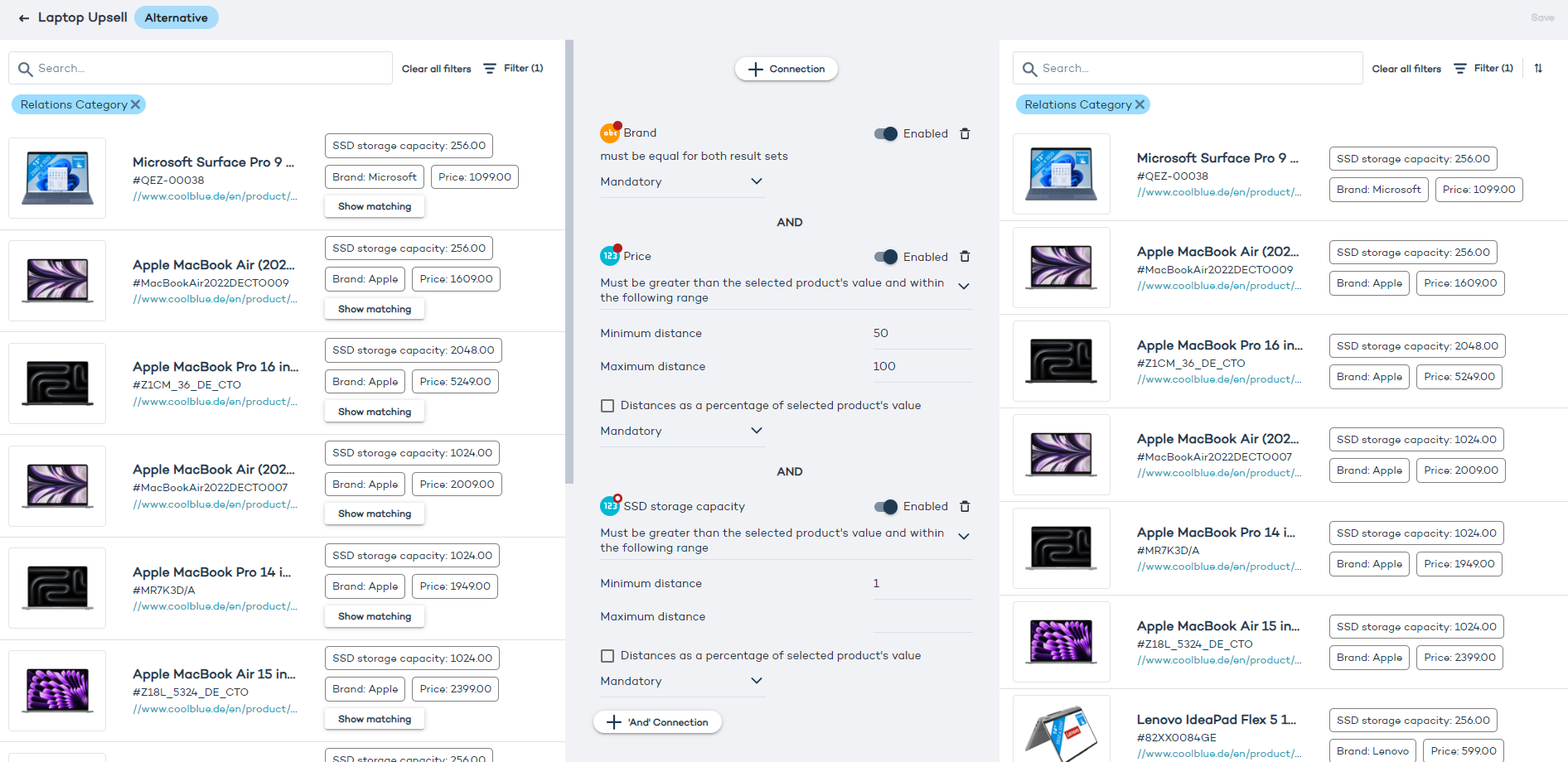
Create an alternative relation to recommend similar products
Alternative relations allow you to link products from the same category (e.g. laptops).
You can create multiple relations of the same type, with different configurations. Use them to create cross- and upselling strategies. For example, recommend laptops with larger storage capacity and slightly higher price.
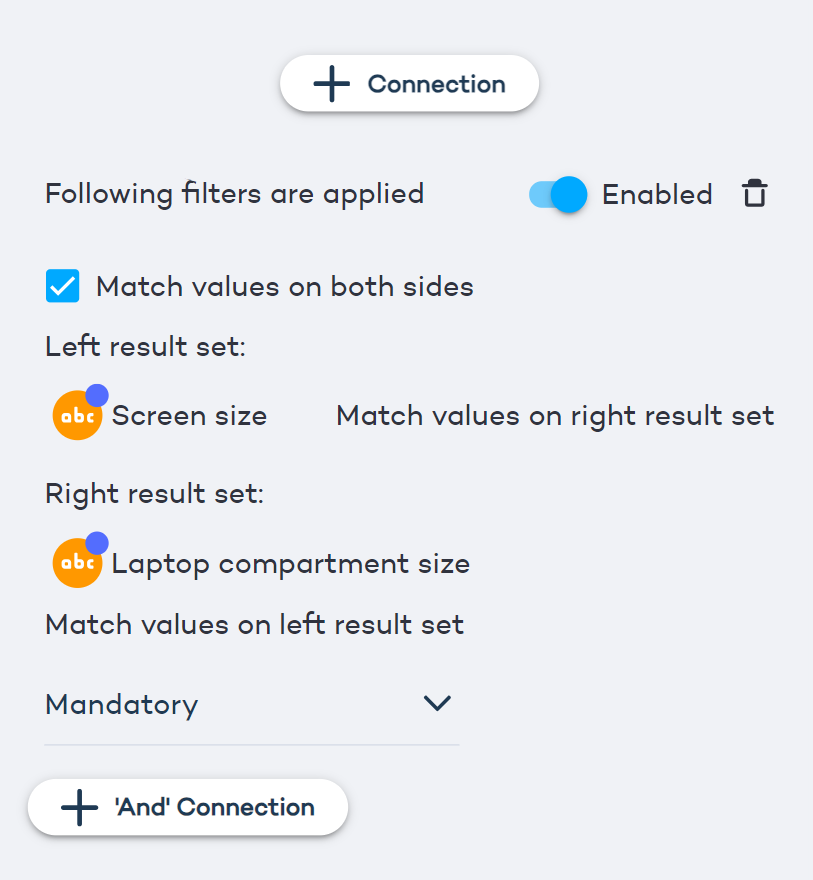
Configure an alternative relation
- Define attributes for left-side and right-side products. Example: the "Brand" attribute's value is "equal for both result sets", meaning that the customer will see only the products by the same brand in their recommendations.
- Decide whether the value is "Mandatory" or "Optional". An "Optional" value may be ignored when there are no matches, resulting in a greater number of less precise recommendations.

- For numeric values (e.g. Price), you can decide whether the linked product's value is greater, less or equal.
- You can then set the minimum and maximum range for your values. For example, if you want to recommended alternative products that are more expensive by no less than 50 and no more than 100 USD, set the minimum distance to 50 and maximum to 100.
- You can click the "Show matching" button next to any product in the left side set to see if it's been linked to any products in the right side set:
